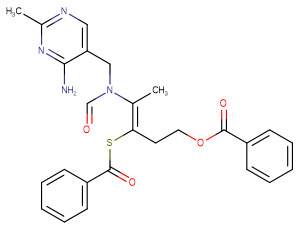
Dibenzoyl Thiamine
CAS No. 299-88-7
Dibenzoyl Thiamine( Bentiamine )
Catalog No. M21353 CAS No. 299-88-7
Dibenzoyl Thiamine a lipophilic derivative of vitamin B (thiamine) is a kind of food additive.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 45 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDibenzoyl Thiamine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDibenzoyl Thiamine a lipophilic derivative of vitamin B (thiamine) is a kind of food additive.
-
DescriptionDibenzoyl Thiamine a lipophilic derivative of vitamin B (thiamine) is a kind of food additive.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsBentiamine
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number299-88-7
-
Formula Weight490.6
-
Molecular FormulaC26H26N4O4S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:98 mg/mL (199.76 mM)
-
SMILESCC1=NC=C(C(=N1)N)CN(C=O)/C(=C(/CCOC(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2)\SC(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3)/C
-
Chemical NameBenzenecarbothioic acid S-(2-(((4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl)formylamino)-1-(2-(benzoyloxy)ethyl)-1-propenyl) ester
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Heywood R Wood JD Majeed SK.Tumorigenic and toxic effect of OS-dibenzoyl thiamine hydrochloride in prolonged dietary administration to rats.Toxicol Lett. 1985 Jul;26(1):53-8
molnova catalog



related products
-
AMAS
AMAS is a nonclaevable heterobifunctional crosslinker with NHS ester and maleimide groups that allows covalent conjugation of amine- and sulfhydryl-containing molecules.
-
Laminin A Chain (209...
Laminin A Chain (2091-2108)
-
Dynorphin B (1-13) (...
Dynorphin B (1-13), a 13 amino acid, is an extraordinarily potent opioid peptide.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


